
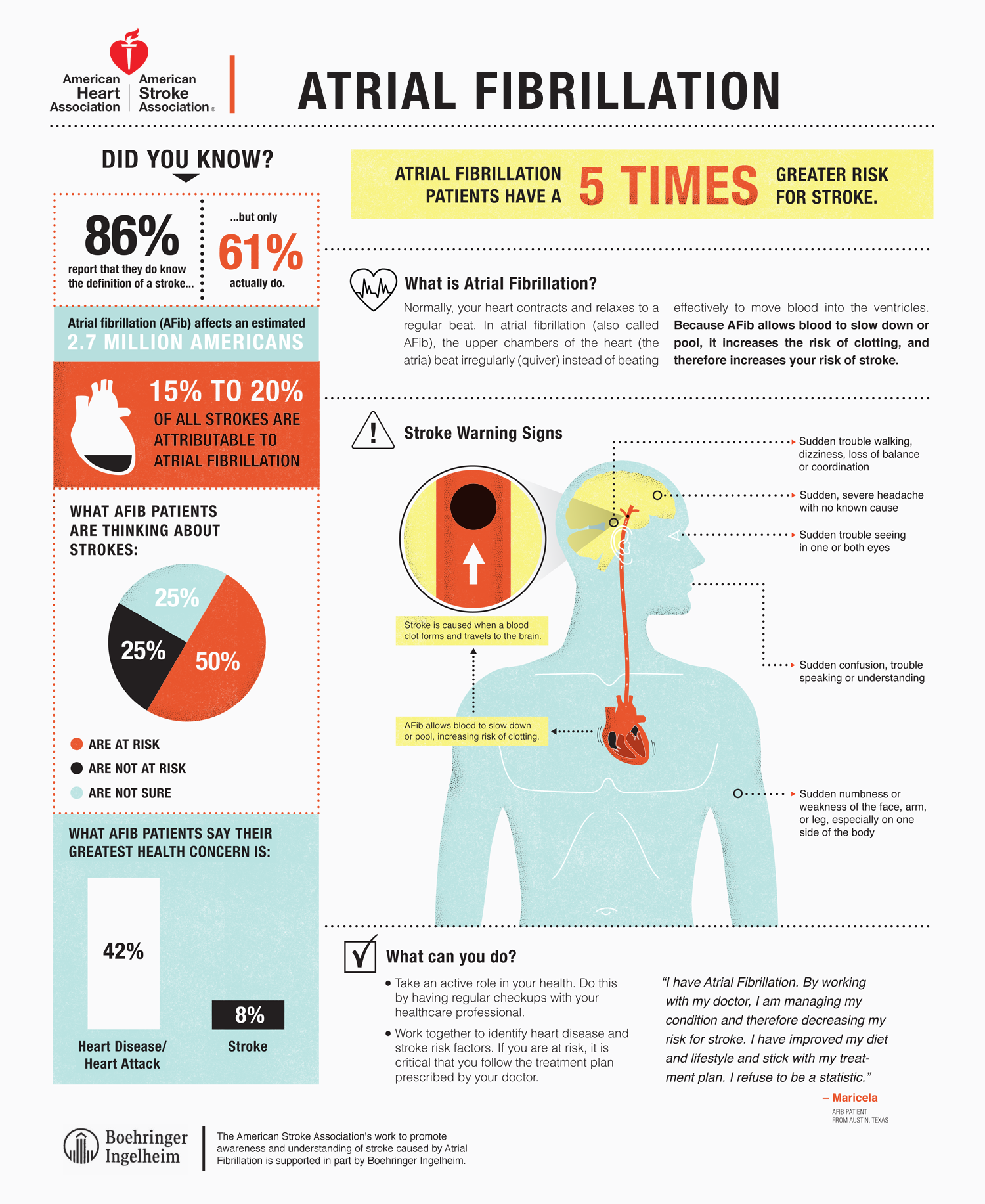
More than 454,000 hospitalizations with AFib as the primary diagnosis happen each year in the United States. Medicine and healthy lifestyle changes to manage AFib risk factors.Blood-thinning medicine to prevent blood clots from forming and reduce stroke risk.Medicines to control the heart’s rhythm and rate.Strokes happen when blood flow to the brain is blocked by a blood clot or by fatty deposits called plaque in the blood vessel lining. Strokes caused by complications from AFib tend to be more severe than strokes with other underlying causes. When standard stroke risk factors were accounted for, AFib was associated with an approximately fivefold increased risk of ischemic stroke. Enlargement of the chambers on the left side of the heartĪFib increases a person’s risk for stroke.High blood pressure, the risk for which also increases with advancing age, accounts for about 1 in 5 cases of AFib. Heart palpitations (rapid, fluttering, or pounding).Others may experience one or more of the following symptoms: Some people who have AFib don’t know they have it and don’t have any symptoms. Because the number of AFib cases increases with age and women generally live longer than men, more women than men experience AFib.People of European descent are more likely to have AFib than African Americans.In 2019, AFib was mentioned on 183,321 death certificates and was the underlying cause of death in 26,535 of those deaths.It is estimated that 12.1 million people in the United States will have AFib in 2030.Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is the most common type of abnormal heart rhythm. Without treatment, AFL can also cause another type of arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation. This can lead to heart failure and long-term disability.
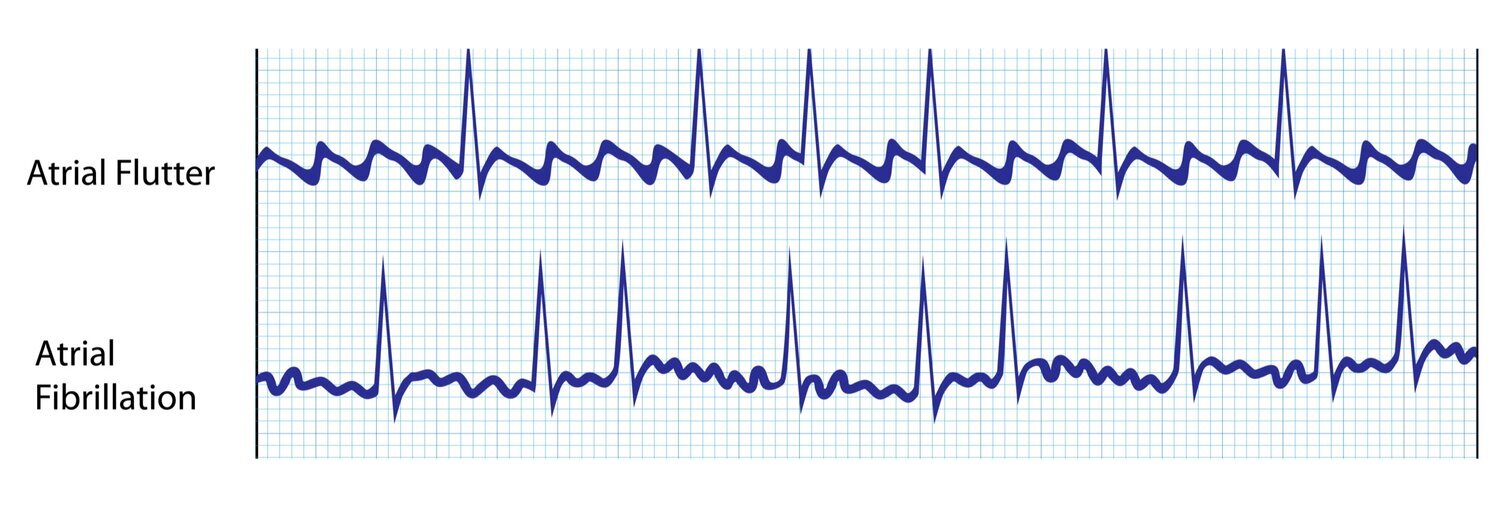
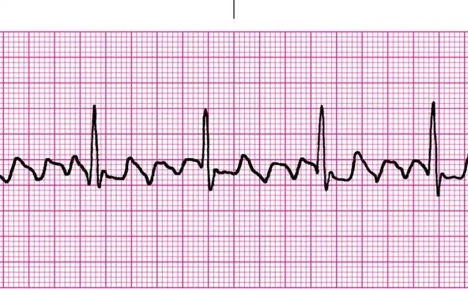
When the ventricles beat too fast for long periods of time, the heart muscle can become weak and tired. This means that the ventricles are beating too fast. Without treatment, AFL can also cause a fast pulse rate for long periods of time. If the clot is pumped out of the heart, it could travel to the brain and lead to a stroke or heart attack. With the blood moving more slowly, it is more likely to form clots. AFL makes it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively. If left untreated, the side effects of AFL can be potentially life threatening. Acquired or congenital valve abnormalitiesĪFL itself is not life threatening.Some medical conditions increase the risk for developing AFL. AFL makes a very distinct "sawtooth" pattern on an electrocardiogram (ECG), a test used to diagnose abnormal heart rhythms. The fast, but regular pattern of AFL is what makes it special. With AFL, the heart beats abnormally fast, but in a regular pattern. In AFib, the heart beats fast and in no regular pattern or rhythm. AFL is a heart rhythm disorder that is similar to the more common AFib. It moves in an organized abnormal circular motion, or "circuit," causing the atria to beat faster than the ventricles of your heart. With AFL, the electrical signal travels along a pathway within the right atrium. This is what causes the pulse we feel on our wrist or neck. As the chambers squeeze and release, they draw blood into the heart and push it back out to the rest of the body and lungs. The electrical current passes through the atrioventricular (AV) node (the electrical bridge between the upper and lower chambers of the heart), causing the ventricles to squeeze and release in a steady, rhythmic sequence. The impulse sends out an electrical pulse that causes the atria to contract (squeeze) and move blood into the lower ventricles. Electrical impulses travel along a pathway in the heart and make the upper and lower chambers of the heart (atria and the ventricles) work together to pump blood through the heart.Ī normal heartbeat begins as a single electrical impulse that comes from the sinoatrial (SA) node, a small bundle of tissue located in the right atrium. The electrical system of the heart is the power source that makes the heart beat.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
